Gynecomastia & Xenoestrogens
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS), perimenopause, and gynecomastia (colloquially, man boobs) are three conditions that would greatly benefit from the removal of xenoestrogens.
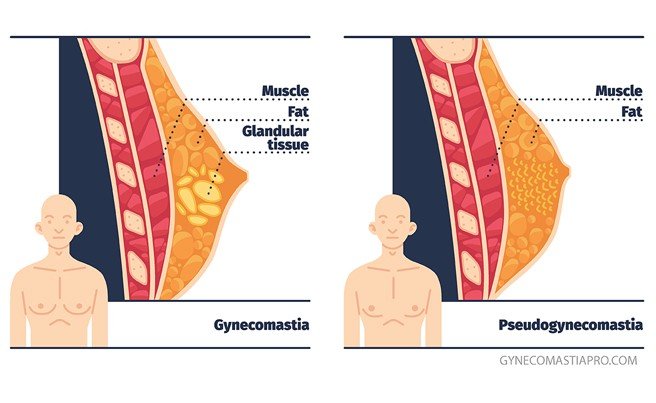
Gynecomastia is the most common breast condition in males that can be caused by an imbalance between the sex hormones testosterone and estrogen. While gynecomastia may look similar in appearance to a related condition called pseudo gynecomastia, there are not the same!
Pseudo gynecomastia: fat deposition without glandular proliferation (aka an increased number of cells in your glands) that occurs most frequently in obese men.
Gynecomastia: likely caused by either “increased use of anabolic steroids or environmental contamination with xenoestrogens or estrogen‐like substances” that causes stimulation of glandular proliferation in male breast tissue.
This condition is often overlooked because males tend to avoid seeking medical attention due to anxiety and psychosocial discomfort, or fear of breast cancer. However, “the incidence of gynecomastia has dramatically increased over the last 20 years, implying that the endogenous or exogenous sex-steroid environment has changed, which is associated with other adverse health consequences in men such as an increased risk of prostate cancer, metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, or cardiovascular disorders” (Koch, 2020). Seeing that there is a rise in gynecomastia, I think this is important to bring up so that it can be discussed in normal conversation without being stigmatized.
During puberty, Estradiol (E2) levels “rise more rapidly than testosterone (T) during early puberty, which leads to an elevated estrogen/androgen ratio,” however, in pre-teen males, this breast enlargement regresses at the same time that testosterone rises and only a small numbers of patients continue to have gynecomastia that usually spontaneously regresses within two years of onset (Cuhaci et al., 2014). However, if the testosterone to estrogen ratio stays imbalanced, either due to increased estrogen production, decreased androgen production or both, gynecomastia may persist. Thus, it is essential to remove and avoid estrogen mimics that can be found in meat, dairy, xenoestrogens, parabens (cleaning and beauty products), plastics (BPA, phthalates), dioxins, and pesticides (DDT, DDE) to lessen the burden of estrogen dominance over testosterone.
Men can boost their testosterone levels to counterbalance their estrogen levels by
Exercising and lifting weights to stimulate muscle growth
Eating a balanced diet of healthy protein, fats, and complex carbohydrates
Minimizing stress and cortisol levels
Sufficient intake of vitamins and minerals such as vitamin D, zinc, and the B complex
Restful and high-quality sleep
Having intercourse
(Mawer, 2016).
-
Cuhaci, N., Polat, S., Evranos, B., Ersoy, R., & Cakir, B. (2014). Gynecomastia: Clinical evaluation and management. Indian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism, 18(2), 150. doi:10.4103/2230-8210.129104
Koch, T., Bräuner, E. V. Busch, A. S., Hickey, M., Juul, A. (2020). Marked Increase in Incident Gynecomastia: A 20-Year National Registry Study, 1998 to 2017, The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 105(10), 3134-3140. https://doi.org/10.1210/clinem/dgaa440
Mawer, R. (2016). 8 Proven Ways to Increase Testosterone Levels Naturally. https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/8-ways-to-boost-testosterone